Total liabilities are the sum of all balance-sheet liabilities, both current and fixed (long-term). Accounts payable, taxes payable, bonds payable, leases, and pension obligations are all included. Also known as Owner’s Equity, is the total amount of assets remaining after deducting all liabilities from the company. Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI’s full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs. This financial document transparently provides investors with crucial information about their equity value.
Calculations Involving Stockholders’ Equity

Remember that a company must present an income statement, balance sheet, statement of retained earnings, and statement of cash flows. However, it is also necessary to present additional information about changes in other equity accounts. This may be done by notes to the financial statements or other separate schedules. However, most companies will find it preferable to simply combine the required statement of retained earnings and information about changes in other equity accounts into a single statement of stockholders’ equity. Small business owners must deal with numerous accounting reports to monitor their business’s finances and ensure its financial health.
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
Often referred to as paid-in capital, the “Common Stock” line item on the balance sheet consists of all contributions made by the company’s equity shareholders. Dividend recapitalization—if a company’s shareholders’ equity remains negative and continues to https://www.bookstime.com/ trend downward, it is a sign that the company could soon face insolvency. A shareholders’ equity ratio of 100% means that the company has financed all or almost all of its assets with equity capital raised by issuing stock rather than borrowing money.
Understanding Shareholder Equity (SE)
- As you can see, net income is needed to calculate the ending equity balance for the year.
- If the same assumptions are applied for the next year, the end-of-period shareholders equity balance in 2022 comes out to $700,000.
- Looking at the same period one year earlier, we can see that the year-on-year change in equity was a decrease of $25.15 billion.
- Treasury shares continue to count as issued shares, but they are not considered to be outstanding and are thus not included in dividends or the calculation of earnings per share (EPS).
- The company can influence equity (in small amounts) by adjusting the dividends paid for the year.
- The shareholders equity ratio measures the proportion of a company’s total equity to its total assets on its balance sheet.
As you might expect, the big changes to retained earnings were net income and dividends. Just as with sole proprietorships and the statement of changes to owner’s equity, the big changes were net income and owner withdrawals. Return on stockholders’ equity, also referred to as Return on Equity (ROE), is a key metric of company profitability in relation to stockholders’ equity. Investors look to a company’s ROE to determine how profitably it is employing its equity. ROE is calculated by dividing a company’s net income by its shareholders’ equity. Understanding stockholders’ equity, how it works, and how it’s calculated can help investors gauge how a company is doing.

This is especially true when dealing with companies that have been in business for many years. Conceptually, stockholders’ equity is useful as a means of judging the funds retained within a business. If this figure is negative, it may indicate an oncoming bankruptcy for that business, particularly if there exists a large debt liability as well.
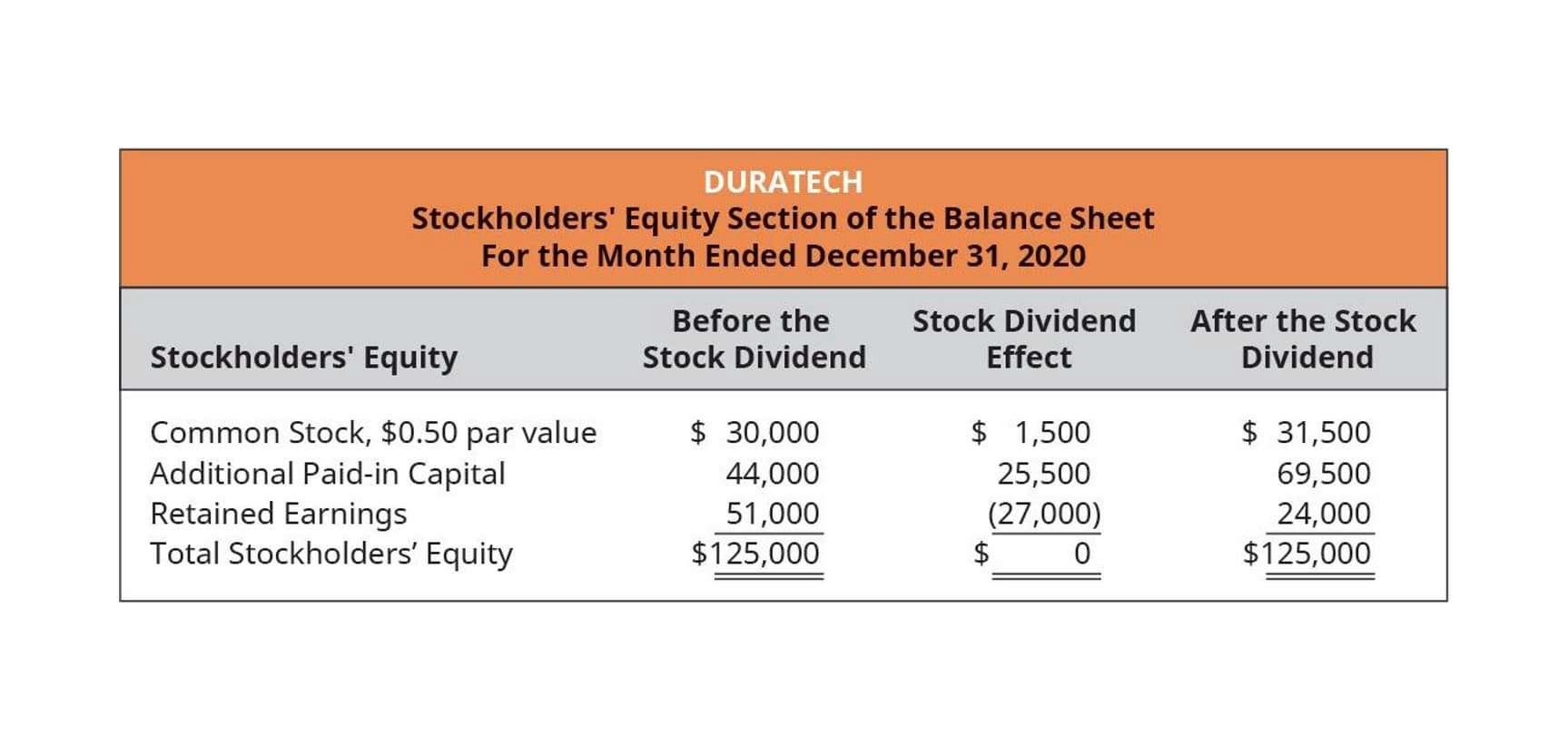
Therefore, cash or other liquid assets should not be confused with retained earnings. If the company chooses to retain profits for internal business investments and expenditures, statement of stockholders equity it is not required to pay dividends to its shareholders. Companies can issue either common or preferred shares, and people can buy these shares to gain ownership of the company.

Outstanding shares are also an important component of other calculations, such as those for market capitalization and earnings per share (EPS). The amount of paid-in capital that a company has is directly related to the total stockholders’ equity that it displays. Shareholder equity represents the total amount of capital in a company that is directly linked to its owners.
Stockholders’ Equity Formula
The fundamental accounting equation states that the total assets belonging to a company must always be equal to the sum of its total liabilities and shareholders’ equity. A statement of shareholders’ equity also can be useful for investors who want more information about a single component of the company’s ownership. Subtracting liabilities from assets can provide investors with the total amount of capital that owners have provided to a company. The third section of the statement of cash flows reports the cash received when the corporation borrowed money or issued securities such as stock and/or bonds. Since the cash received is favorable for the corporation’s cash balance, the amounts received will be reported as positive amounts on the SCF. Shareholder equity (SE) is a company’s net worth and it is equal to the total dollar amount that would be returned to the shareholders if the company must be liquidated and all its debts are paid off.
- It helps them to judge the quality of the company’s financial ratios, providing them with the tools to make better investment decisions.
- In recent years, more companies have been increasingly inclined to participate in share buyback programs, rather than issuing dividends.
- Since total assets rose $95,000 versus a $101,000 increase in total liabilities over the period, the company’s stockholders’ equity account actually dropped in value by $6,000.
- It might sell the stock at a later date to raise capital or it might use it to prevent a hostile takeover.
- Other comprehensive income includes certain gains and losses excluded from net earnings under GAAP, which consists primarily of foreign currency translation adjustments.