Unfortunately, many companies may feel closed out of this approach due to the constraints imposed by the fair value hedge accounting rules. The good news is that a work-around may be available for these companies. In this instance, however, cash flow hedge accounting is the appropriate choice. Under cash flow hedge accounting, effective hedge results are initially recorded in Other Comprehensive Income (OCI) and later reclassified to earnings, coincidently with the sales recognition. If that derivative is used as a hedging tool, the same treatment is required under IAS 39. However, this could bring plenty of volatility in profits and losses on, at times, a daily basis.
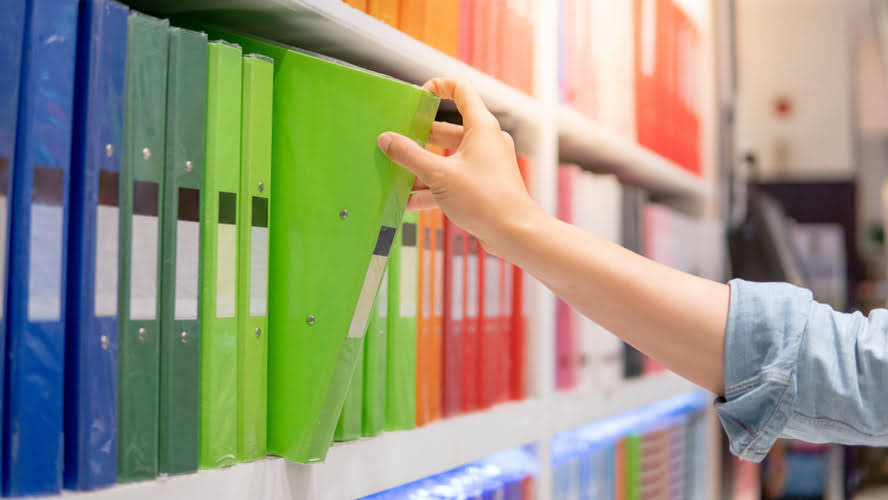
In some instances, a business may also hedge inventory because a deal or promotion is too good to pass up. In this article, we’ll define hedging inventory, discuss when a business should consider inventory hedging, and review the risks of ordering too much inventory. Buying hedges are speculative trades and carry the risk of being on the wrong side of the market, in which case the investor could lose some or all of their investment. Put options for broad indexes are cheaper than individual stocks because they have lower volatility.
Option Pricing Determined by Downside Risk
Sarah assumes that the price will go up, but in the event that the stock value plummets, Sarah can pay a small fee ($7) to guarantee she can exercise her put option and sell the stock at $10 within a one-year time frame. Until recently, Pershing Square held about 1.2 million shares of Lowe’s hedge inventory (LOW 0.47%) in a stake valued at $286 million — but no more. By the time the hedge fund’s annual report came out in February, it revealed that Ackman had sold the remaining portion of his position. Pershing had maintained its stake in Lowe’s since 2018, generating $1.8 billion in profit.
The Hedge Fund in Your Pantry – Kellogg Insight
The Hedge Fund in Your Pantry.
Posted: Mon, 01 Apr 2024 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The risk of using the buying hedge strategy is that if the price of the commodity drops, the investor may have been better off without buying the hedge. Options allow investors to hedge their positions against adverse price movements. If an investor has a substantial long position on a certain stock, they may buy put options as a form of downside protection. If the stock price falls, the put option allows the investor to sell the stock at a higher price than the spot market, thereby allowing them to recoup their losses.
Get Started Today!
This step involves determining the optimal level of safety stock to handle unexpected demand spikes or supply delays. It serves as a buffer to mitigate stockouts and maintain customer service levels. Let’s look at some basic examples of the futures market, as well as the return prospects and risks. Thus, if a profit is taken on a derivative one day, the profit must be recorded when the profit is taken. If you own a home in a flood-prone area, you will want to protect that asset from the risk of flooding—to hedge it, in other words—by taking out flood insurance.
This inventory caters to predictable, often seasonal, demand spikes to ensure the production process remains uninterrupted and customer needs are met during peak seasons. Over 1.8 million professionals use CFI to learn accounting, financial analysis, modeling and more. Start with a free account to explore 20+ always-free courses and hundreds of finance templates and cheat sheets.
Three types of hedging relationships
Remember that purchasing widespread excess inventory to “hedge” against inflation is often considered risky. Most businesses that purchase hedge inventory identify particular concerns about specific items on their inventory lists. When the prices of all supplies are the main concern, most companies instead renegotiate with their suppliers, raise prices for their customers, or both. Say a rice cake manufacturer has become aware that a severe drought is expected to drastically reduce rice supply by the second half of the calendar year.
TrendyWear Fashions analyzes past sales data to estimate selling 300 denim jackets, 400 dresses, and 250 pairs of sneakers monthly. Last fall, TrendyWear sold 450 denim jackets due to cooler weather which aids in preparing inventory for the upcoming season. A higher turnover ratio indicates efficient inventory management and sales processes.
What Is a Commercial Hedger?
Although it may sound like the term “hedging” refers to something that is done by your gardening-obsessed neighbor, when it comes to investing hedging is a useful practice that every investor should be aware of. In the stock market, hedging is a way to get portfolio protection—and protection is often just as important as portfolio appreciation. To properly hedge inventory, it is essential to have a strong hedging policy, uniform hedge financial reporting, a control system with accurate targeted reporting, as well as professional advice and risk modeling. Economic neutrality is maintained because the valuation of the stock can be readily countered by the reverse valuation of the active future hedge; however, what occurs to cash flow?